ICT Security Basics from Trust to Blockchain Course
H1
Summary of Hutchins et al 2011: Intelligence-Driven Computer Network Defense Informed by Analysis of Adversary Campaigns and Intrusion Kill Chains paper.
- The paper presents a framework that can be used by both parties - attackers and defenders.
- The framework contains several steps that are organized in a chain, so if one step in this framework was missed, then the chain “breaks”. To perform successful attack or defense all these steps should be taken in an order that they are described.
Framework includes 7 steps:
- Reconnaissance - research and information gathering.
- Weaponization - for example pairing remote access trojan and a payload.
- Delivery - delivering payload to the target, for example via USB stick that can be dropped on the street or handled to the target, or a malicious link that victim clicks.
- Exploitation - for example with a USB stick, the mallwear that installed on the USB stick can start to execute automatically after it was inserted into the computer aka USB Rubber Ducky. (Source: https://shop.hak5.org/blogs/usb-rubber-ducky)
- Installation - installation of the backdoor that an attacker can use for remote access.
- Command and Control (C2) - establishing the connection between the attacked target and command control server.
- Actions on Objectives - at this stage actual goals can be achieved: stealing or destroying the data etc.
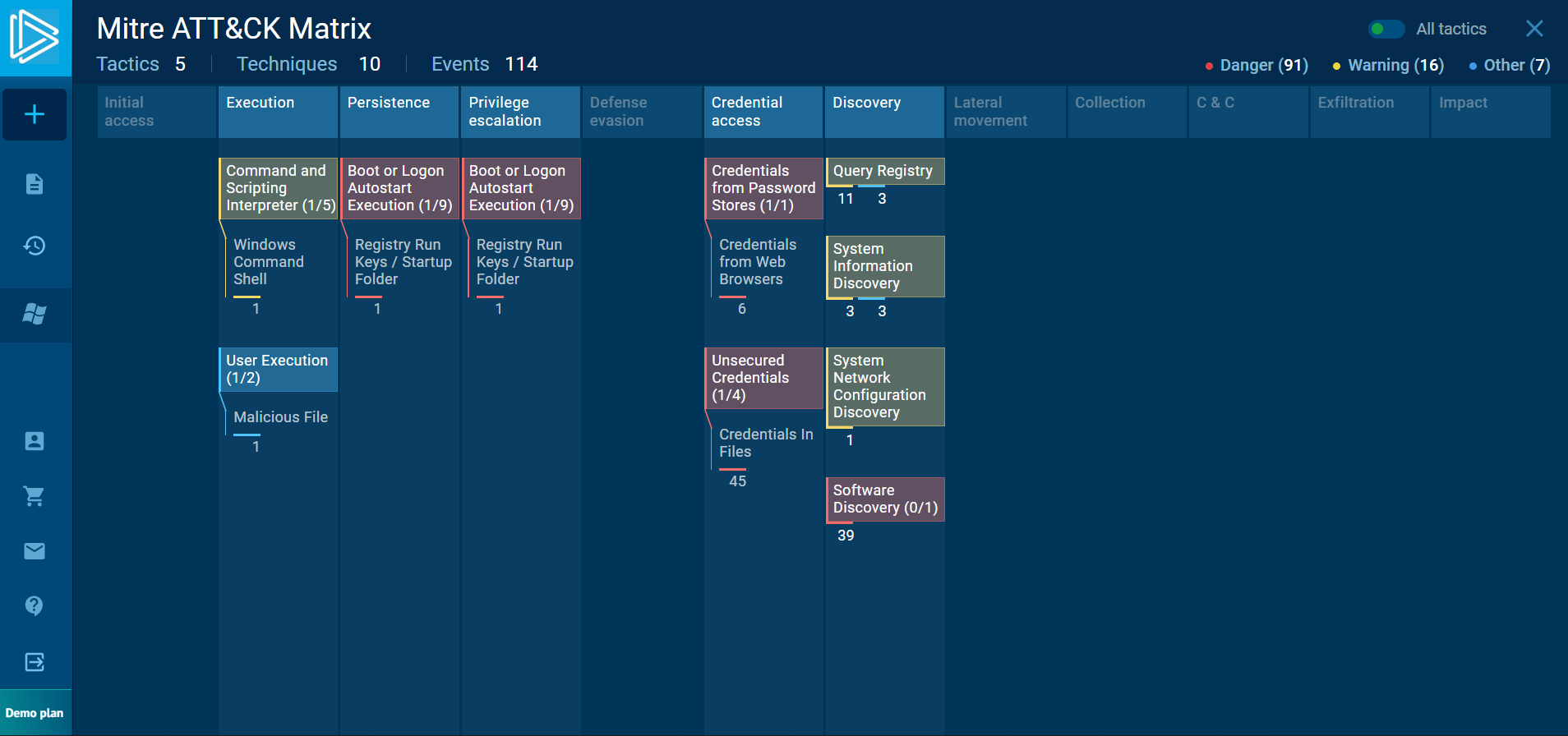
Mitre Att&ck Framework
Mitre Att&ck Framework is more detailed and describes different tecniques and sub-tenchinques. It’s not strictly stuctured as Cyber Kill Chain. Also it containes different Matrixes for different entities, such as separate Enterprise Matrix that contains sub-categories such as Windows, macOS ets. Mitre Att&ck Framework has separate Matrix for Mobile and Matrix for Industrial Control Systems.
Table 1. Mitre Att&ck Framework Enterprise Matrix Summary. Source: What is Mitre Att&ck Framework? - Definition (cyberark.com)
| Tactic | The Adversary is Trying to: |
|---|---|
| Reconnaissance | Gather information they can use to plan future operations |
| Resource Development | Establish resources they can use to support operations |
| Initial Access | Get into your network |
| Execution | Run malicious code |
| Persistence | Maintain their foothold |
| Privilege Escalation | Gain higher-level permissions |
| Defense Evasion | Avoid being detected |
| Credential Access | Steal account names and passwords |
| Discovery | Figure out your environment |
| Lateral Movement | Move through your environment |
| Collection | Gather data of interest to their goal |
| Command and Control | Communicate with compromised systems to control them |
| Exfiltration | Steal data |
| Impact | Manipulate, interrupt, or destroy your systems and data |
Comparison of Cyber Kill Chain and ATT&CK Enterprise matrix
First of all, the ATT&CK Enterprise matrix is more detailed, it contains more steps in the chain and also possible techniques and sub-techniques. But the Cyber Kill Chain and ATT&CK Enterprise matrix have the same backbone, the difference is just ATT&CK Enterprise matrix has several steps that can fit in one in the Cyber Kill Chain.
Another difference is that the Cyber Kill Chain has a defined order, “where adversaries are expected to move linearly from one phase to another. The MITRE ATT&CK Framework is deliberately unordered to acknowledge that an adversary may move through Tactics out of order, skip some Tactics, and revisit some Tactics multiple times throughout the course of an attack.” (Poston, H. 2020. How to Use the MITRE ATT&CK® Framework and the Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain Together, https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/topic/how-to-use-the-mitre-attck-framework-and-the-lockheed-martin-cyber-kill-chain-together/)
I think that both attackers and defenders can benefit from these models. As well as other stakeholders of the business. In my opinion MITRE ATT&CK Framework could be useful in learning what kind of attacks are possible and what are the risks of the business.
What is missing from these models? I couldn’t find a step in the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix about stealing the data.
Security incident description and analisys
Cloud Hopper, episode 103, Darknet Diaries.
Source: https://darknetdiaries.com/episode/103/
Some company was informed by the Swedish Security Service that their computer was reaching out to some known bad source. Turned out that it was the jump server of the MSP, the server that was used to manage many customers, was reaching out to some command and control server.
MSP works by taking on other enterprises as clients, they monitor and patch their services if needed. Source So finding a breach in such a thing as a jump server was a really bad thing for the MSP.
“A jump server is defined as a system on a network that accesses and manages all the devices in a different zone of security.” - Source
To start the investigation, a threat analyst from Truesec received disc images and a memory dump from the attacked server. Because the antivirus didn’t trigger, he started to check manually. The first thing he checked was the /temp folder. Temp folder is used to store temporary files. Source VG. 2012
The file that was the output of the mimikatz software was discovered in the temp folder. Mimikatz is used to extract pins, hashes and passwords from the memory. Source. And it was a Windows server, which has a known vulnerability. It keeps passwords that are used to login in the memory, sometimes in plain text.
After scanning memory and disc for the IP address that was given to them by Swedish Security Service of this malicious command and control server. They found a process that was connected to this server. It was a legitimate software that scans for rootkits. But it was in an unusual location. And next to that file there were several dll files. So threat analysts suspected dll side-loading.
“DLL side loading is an attack where malware places a spoofed malicious DLL file in a Windows directory so that the operating system loads it instead of the legitimate file.” Source
Also they found an executable file - nbt.exe, it’s a legitimate file that is used to scan networks and it’s how windows computers connect to shared network drives. Another file had a list of public IP addresses that were scanned. Turned out that some of these IP addresses belonged to the US Department of Defense. Another malware was found on the server and it was PlugX, PlugX is a known RAT (Remote Access Trojan) and it can control the computer remotely.
Also they found out that the attack was running for weeks. And because the attack was running already for a long time. They tried not to reveal that they found out the breach and didn’t kill the process, because it’s easy to work on an attack that is ongoing, and attackers won’t be able to react.
In the end it turned out that somebody planted the malware from the MSP premises using stolen credentials of the MSP employee.
In short, the threat actor wanted to get into the US Department of Defense network, so they decided to hack MSP, hoping that some of the MSP customers would be connected by NetBIOS to the US Department of Defense, so they could get access. So the attackers did have an advanced persistent threat or APT.
“Advanced persistent threat is a covert cyber attack on a computer network where the attacker gains and maintains unauthorized access to the targeted network and remains undetected for a significant period”. - Cisco. What Is an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)
The hack was associated with the Apt10 group. Source. Thousands of social security numbers were stolen, as well intellectual property in order to gain the competitive advantage.
To fix the breach MSP had to change all the passwords, which took lots of time and effort.
Analysis
Reconnaissance There is no information about the Reconnaissance phase, but threat actors definitely conducted Active Scanning and Gathering Victim Host Information to define that the target server was running Windows, it helped them to plant mimikatz, the software that targets Windows systems.
Resource Development Also we know that credentials for the jump station were compromised from the MSP employee, so probably it was done by using some Phishing techniques. Credentials of the jump station were stolen to plant mimikatz.
Initial Access At this stage attacks used the Valid account of the MSP employee.
Execution At this point attackers were collecting credentials of users that were connecting to other servers via this jump station. So attackers needed some User Execution. For the second stage, when attackers used a DLL loading attack, the Shared Modules technique was used. Persistence Attackers were really successful at this stage. The attack was running for several weeks without being noticed. Hijack Execution flow was used when malicious dll was placed using Valid Account.
Privilege escalation Attackers used Create or Modify System Process technique and Hijack Execution flow, when they installed mimikatz, rootkit and RAT using Valid Account and RAT.
Defence evasion Trusted Developer Utilities Proxy Execution was used. Payloads that were placed on the target server were legitimate software. Also valid account credentials were used.
Credential Access Input capture was used to get credentials for other servers that were accessed via compromised jump server. The first login to the jump server was done from MSP premises using stolen credentials of the MSP employee.
Discovery To attack the jump server, threat actors might have used System owner/user discovery to steal MSP employee credentials. For the next stage of the attack Network Service Scanning was used to see if there are servers in this Network that are connected to the Department of Defense.
Lateral Movement Attackes used Remote Services to connect to the server. (PlugX trojan)
Collection Input Capture was used to steal credentials via keyloggers. Data From Local System, the file with credentials that was created by mimikatz was accessed.
Command and Control Remote Access Software was used, particularly PlugX trojan.
Exfiltration Exfiltration Over C2 Channel was used.
Impact Various data was stolen from customers of the attacked MSP. As well as data from the Department of Defense including social security numbers of the US Navy. (For some reason MITRE Matricx doesn’t have anything about stealing the data).
Install Debian on VM

H2
Summary of Santos et al 2017: Security Penetration Testing - The Art of Hacking Series LiveLessons: Lesson 6: Hacking User Credentials
Vulnerable passwords are:
- Default passwords, passwords that products are shipped with, for example modem or switch passwords. Default passwords must be changed
- Simple passwords. For example: cat, qwerty, 12345678, date of birth. Longer and more randomized passwords with special characters must be used as well as two factor authentication if it’s available
- Reused passwords. Using the same passwords across different accounts is not secure. Using different passwords for different account
- Admin password. After cracking the admin password, access to the whole system will be compromised. Using secure admin password, change it regularly, use two factor authentication
Ways of stealing the password
- Wifi spot in the hotel or cafe, we don’t know how the network is set up, when we are visiting a hotel or a cafe and using their password. There are several types of attacks that could be conducted. For example traffic sniffing and man-in-the-middle attacks. I was wondering about this, isn’t it really difficult to do nowadays (I’m not talking about websites that still use http), because all the traffic should be encrypted and while sniffing traffic you just get bits and pieces of information? For example when using nmap. Is there really a way to make sense of that easily?
- SSL spoofing
- SSH downgrade
- Compromising switch or modem (for example using the default password)
Why is it easy to crack passwords?
- Using modern CPUs and GPUs made the process of cracking password hashes faster
- We can use distribution between machines nowadays.
- Dictionaries. There are many password dictionaries out there. They are collected from the most used passwords and password breaches.
- Weak algorithms. For example Windows’ nt hash and lm hash. Or not using the salt in passwords. (Using salt in passwords will prevent two users having the same password hashes if they have the same password)
How to improve password security?
Consumer:
- Use two factor authentication
- Use certificate based authentication
- Use better longer passwords
Company:
- Use encryption
- Use hashing
- Use salt
- Secure password storage
- Support longer passwords with special characters
Cracking hashes
- 21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc3 = admin
- f2477a144dff4f216ab81f2ac3e3207d = monkey
-
$2y$18$axMtQ4N8j/NQVItQJed9uORfsUK667RAWfycwFMtDBD6zAo1Se2eu. Hash is bcrypt $2*$, Blowfish (Unix). Hashcat mode: 3200. Estimated time for cracking with VM box id 7 years :)

- I don’t have any physical linux machine right now to test how hashcat uses GPU. Tried with my Raspberry Pi400, but didn’t work, the error was No devices found, the command I tried to use was hashcat -m 0 -d 2 ‘somehash’ rockyou.txt -o solve, where -d 2 is specifying device type GPU.
- Tried to crack sha256 hash of simple password that I found in the dictionary “happy5”, so Raspberry Pi400 cracked it straight away. Was having problems in the beginning, forgot to use -n when hashing.
Something to think about: we just learned that hashing is a one-way function. If this is true, why can you crack the hash and find out the original password?
Because we are not cracking the hash itself, but using the hash algorithm to hash password from the pasword lists and then comparing these two hashes.
Summary of Schneier 2015: Applied Cryptography: Chapter 2 - Protocol Building Blocks
- Protocol is a predefined chain of steps, that should be accomplished by at least two parties.
- There are three types of protocols:
- Arbitrated. When parties use some trusted third party that will verify the data.
- Adjudicated. When parties use a trusted third party to solve the conflict in the case if one of the parties cheated.
- Self-enforcing. Cheating of any party included in the communication is immediately detected.
- Types of protocol attacks:
- Active attack - requires active intervention. Corrupting data, gaining unauthorised access to resources. Follow the protocol, but try to obtain more information than protocol allows.
- Passive attack - collect information about communicating parties, capturing messages. Disrupt protocol.
Public-key cryptography
The protocol was designed by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman in 1976 and it changed that paradigm of cryptography forever.
Key exchange process

- First user A and user B use public variables and combine their private key with the generator. So user A will have A + G = AG and user B B + G = BG.
- Exchange these variables AG and BG. So user A gets BG and user B gets AG.
- User A takes BG and combines it with his private key. And user B combines AG with his private key. So user A now has BGA and user B AGB.
- Now this key can be used for further communicaton.
Nothing from the public area can be combined to get the private key value. And the private key is never shared or never gets into the public area.
Source: Secret Key Exchange (Diffie-Hellman) - Computerphile https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NmM9HA2MQGI
H3
Summary of Schneier 2015: Applied Cryptography Chapter 1: Foundations
-
Cryptography not only provides confidentiality but is also used as an authentication (when the receiver can prove the origin of the message). Integrity - when the receiver is sure that the data wasn’t changed while transferring. And nonrepudiation - when the sender can’t deny that he sent a message.
- There are two types of key-based algorithms.
- Symmetric - where the decryption key can be calculated from the encryption key and vice versa. In most symmetric algorithms decryption and encryption keys are the same. Symmetric algorithms are divided into stream algorithms that operate on the plain text a single bit at a time, and block algorithms that operate on the plain text in groups of bits.
- And another type of key-based algorithm is asymmetric when encryption and decryption keys are different. Public key - encryption key. Private key - decryption key.
- Messages could be hidden in the images.

(Source Hide Your Message Inside the Image : 5 Steps - Instructables copy /b some.jpg + msg.txt hiddenmsg.jpg)
- Three most common cryptographic algorithms
- Data Encryption Standard (DES) - symmetric algorithm
- RSA - public-key algorithm, used both for encryption and digital signatures.
- Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) - used only for digital signatures
Examples of public-key cryptography.
-
TLS (Transport layer security) (application layer) - protocol for establishing encrypted communication between computers. Before TLS the data on the web was transmitted in plain text. SSL certificate - digital document that identifies the website using key pair. The public key allows a web browser to initiate an encrypted communication with a web server using TLS and HTTPS protocols. Private key is kept secure on the server and used to digitally sign web pages and other documents (js files, images). It also identifies info about websites. (Source: ssl.com)
-
IPsec (Internet layer) - a group of protocols that are used together to set up encrypted connections. For example it is used for setting up VPN. It encrypts IP packets and authenticates the source from where this packet came from. (Source: What is IPsec? How IPsec VPNs work. Cloudflare) IPsec uses Digital Certificates. Digital certificate - is a document that is issued by Certificate Authority. The certificate contains a general public key for a digital signature and specifies the identity of the key owner. (Source: How does the IPsec use digital certificates and digital signatures? (tutorialspoint.com)).
Encrypting and signing a message




H4
Summary of Shavers & Bair 2016: Hiding Behind the Keyboard: The Tor Browser.
- Tor browser (that was built based on Firefox) anonymises users and makes tracking them if not impossible, but extremely difficult.
- Tor browser hides the user’s IP address.
- Tor doesn’t keep any internet history.
- Tor nodes are publicly available and some resources can be used to search if this IP is or was used as a Tor node (Exonera Tor)
- Because Tor is a portable application (it can be run from anywhere, including a USB stick), users tend to hide it by changing the name of the execution file and placing it in a random place on the computer. So during the investigation, it’s important not only to search for “tor” on the computer but also tor hashes.
- Another thing that makes Tor browser difficult to investigate is how it uses memory. After the Tor browser is shut down, it cleans up the memory. But while Tor is running, the remnants of URLs could be retrieved, they stay in memory for a couple of minutes.
- Windows stores the presence of Tor browser C:\pagefile.sys, so it can be used to investigate if the Tor browser was used on this computer. Also visited websites can be retrieved from it.
- Prefetch, which speeds up the loading of the applications in Windows can be unitised to see if Tor was running.
- Mainly if a user’s anonymity gets compromised in Tor it happens because of the user’s mistake. For example not disabling javascript, downloading a file and opening it locally or clicking the button that allows tracking the location. All these actions will lead to the IP address being disclosed.
- There are Hidden services in the Tor network. Hidden services provide email or file hosting. They are not indexed by search engines and that’s why they are invisible on the Internet. Hidden services don’t use exit nodes, so they use end-to-end encryption. Setting up a hidden service is a fairly easy task.
Installing Tor

Searching in Dark Web
-
Search engine

-
Marketplace

-
Fraud

-
Forum

Anonimity compromise case in Tor
Since 2020 threat actors was placing malicious exit nodes to perform SSL stripping attacks on users who were accessing cryptocurrency-related sites. It was reported that in May 2020, they ran a quarter of all Tor exit relays. SSL stripping attack is the attack when a user’s traffic is downgraded from using HTTPS to HTTP. The primary goal of this attack was to replace bitcoin addresses.
“Bitcoin mixers are websites that allow users to send Bitcoin from one address to another by breaking the funds into small sums and transferring them through thousands of intermediary addresses before re-joining the funds at the destination address. By replacing the destination address at the HTTP traffic level, the attackers effectively hijacked the user’s funds without the users or the Bitcoin mixer’s knowledge.” (Source: https://www.zdnet.com/article/a-mysterious-group-has-hijacked-tor-exit-nodes-to-perform-ssl-stripping-attacks/)
Other networks from Tor
Other networks than Tor. For example, there is ZeroNet. It is a decentralized peer-to-peer network. Instead of having the IP address, the website is identified by a public key. And the owner of the website, having a private key, can add changes there. Zero net uses Bitcoin cryptography, it’s not anonymous by itself but it can route the traffic through the Tor network. The killer feature of ZeroNet is the possibility to browse websites even without an internet connection. (Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ZeroNet?msclkid=0d91920bc3a311ecb55b7af6c42d4053)
How does anonymity work in Tor?
The security of Tor is in its essence to direct the traffic through randomly chosen relays. It also uses elliptic curve cryptography. The traffic is encrypted starting from the first relay, and then the second relay strips the first layer of the traffic and sends it to the next relay. It continues till the last exit node that passes unencrypted traffic to the destination. The exit node changes every 10 minutes.
Tor threat models
Tor can be used in Reconnaissance, so the target won’t be able to identify the IP address while the threat actor brows website. Or threat analytic can conceal his IP so the target won’t see that there was a connection from the police or some governmental office. Also, Tor can be used for phishing attacks using hidden services for sending an email.
H5
Summary of Felten et al 2015: Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Technologies,
- For bitcoin hash function need to have three security properties:
- collision free - nobody can find the value of x and y, and yet the hash of x and hash of y are equal. Collision still exists, because the amount of possible inputs are more than possible outputs (256 possibilities). How to find a collision:
- hiding - if we have an output of the hash function it’s infeasible to find the input. It doesn’t work if there are only a couple of possible input values, then it’s easy to find the input from the output.
- puzzle-friendly - for every possible output of the hash function, if the key is chosen randomly from the set that is widespread out. it is impossible to find the value that hits exactly the target.
-
Hash pointer - pointer to where the information is stored and cryptographic hash of the info (we can get the information back and verify that the information hasn’t changed)
-
Merkle tree is the binary tree build with the hash pointers, it’s very efficient and we can prove that the data wasn’t changed by “showing” less data than in the case of a blockchain
-
Hash pointers can be used in any pointer based data structure, if the data structure doesn’t have cycles.
-
Bitcoin uses elliptic curve signature algorithm (ECSA)
- There are three steps of digital signature:
- First we generate public and private keys. Public keys are shared and private keys should be kept secret.
- Second step is a sight operation. For generating digital signatures, we need a public key and a message.
- Last step is a signature verification. Public key is required to verify a signature. The operation takes message and public key of the person who signed the message and verifies if the signature is valid or not.
- Double spending attack is when the same coin is spent twice.
Summary of Nakamoto, Satoshi 2008: Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
- Satoshi Nakamoto in the paper described a system that doesn’t rely on trust and solves the double-spending problem.
- The system allows non-reversible transactions and lowers the cost of the transaction itself.
- Before that there were no systems that could support payments over a communication channel without a trusted party.
- Transaction - bitcoin is a chain of digital signatures in its essence. Each owner of the coin signs a hash of the previous transaction, public key of the next coin owner and adds this signature to the end of the coin on transfer. The ownership of the new block can be verified because the information of the previous block is stored in the new block.
- Timestamp server - every block in Bitcoin has a timestamp used in hash with other information.
- Proof-of-work - is a process of verifying the transaction. It uses the piece of data that is costly to produce, but easy to verify. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 hashing algorithm in its proof-of-work to verify the transaction.
- Network - nodes always consider the longest chain to be correct. The network flow looks like this - first the transaction is broadcasted to all nodes, every node tries to solve proof-of-work, when the node finds the proof-of-work it broadcasts it to all nodes. Other nodes accept the block only if all transactions were valid and weren’t spent. After accepting the block nodes use the hash of the newly created block to use it in the next block.
How much is one BitCoin (BTC) worth now?
The price of bitcoin on 01.05.22 (10:53) Finnish time is 37 991.73 dollars for one bitcoin.
If I would buy bitcoin on 8 of November in 2021 when bitcoin was all time high, I would lose lots of money in the next couple of month.

Or if I would buy Bitcoin on 21 of September in 2020, when Bitcoin costs 10 601 dollars, I would gain a lot in the next several months.

(Source: #1 Bitcoin Price History Chart (2009, 2010 to 2022))
Is it legal to own BitCoin in Finland?
It is legal to own Bitcoin in Finland. Bitcoin is treated as a commodity in Finland and not as a currency. Also there are tax rules for bitcoin in Finland. When trading Bitcoin, it’s treated as a capital gain. On the other hand, when used as a payment for goods and services, Bitcoin is treated as a trade. (Source: 9 Exchanges to Buy Crypto & Bitcoin in Finland (2022)) (Source: Legal Status of Bitcoin. NewsBTC)
What’s a block chain?
Block chain is a decentralized hash pointer based data structure, where blocks are connected and the next block keeps the information about data of the previous block. So if one of the blocks in the chain is modified it will be detected straight away.
Altcoins
Cardano (ADA) is an altcoin developed by a group of researchers and scientists. The main advantage of Cardano is that it uses less energy to compute the next block, therefore is more sustainable than Bitcoin. (Source: What is Cardano? | Coinbase, https://www.cardano.com) Also Cardano has smart contracts. Cardano is built on Ouroboros proof-of-stake consensus protocol.
“Ouroboros is a Proof of Stake (PoS)-based permissionless consensus protocol for cryptocurrencies. It is deployed as part of Cardano, which has a cryptocurrency called ADA associated with it. The basic idea in PoS is to replace the energy-expensive Proof of Work (PoW) common in first generation Blockchain protocols such as Bitcoin and the current version of Ethereum (although Ethereum has its own PoS protocols under development), with a lighter-weight mechanism where each node’s probability of being a block producer is proportional to how many coins it has.” - Bhaskar Krishnamachari. (Source: Formalizing Proof of Stake-based Consensus: Ouroboros | by Bhaskar Krishnamachari | Medium) Currently the best Bitcoin altcoin is Ethereum. Etherium is not only a currency but also a programmable blockchain.
H6
Felten et al 2015: Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Technologies, videos Week 2 summary
- There are no systems that are purely centralized or decentralized. (Ex. email)
- Aspects of decentralization in Bitcoin
- peer-to-peer network - the part of the bitcoin that is purely decentralized, anybody can run bitcoin node.
- mining - requires high capital cost, so it has high centralization.
- updates to software - there are core developers that are controlling which software would be released.
- Distributed consensus
- Key challenge to build a decentralized e-cash system is called distributed consensus.
- The protocol should terminate and correct node should agree upon value.
- And this value should be proposed by one of the current nodes.
-
When somebody pays someone in the Bitcoin network, the transaction is broadcasted to all Bitcoin nodes. The payer signature includes a payee public key, and a hash - way for payer to link together receipt and the coin that she received previously.
- How does it work in Bitcoin?
- All nodes have a sequence of blocks of transactions they’ve reached consensus on.
- Each node has a set of outstanding transactions that it’s heard about
- Why consensus is hard?
- Nodes can crash or be malicious.
- Network is imperfect.
- Not all nodes are connected, faults in network and latency.
- No notion of global time. (because nodes are spread in the interned, nodes can’t agree on the timestamp)
- Bitcoin consensus works better in practice than in theory:
- Because bitcoin can reward the nodes to act honestly.
- Embraces randomness.
- The longer consensus protocol runs, the the more probability that the transaction is valid goes higher, and if it’s not - goes down exponentially.
- How does bitcoin work when nodes don’t have identities?
- Bitcoin consensus algorithms.
- Bitcoin nodes don’t have identity, because it’s P2P system and to avoid Sybil attack. (number of fake identities controlled by one real identity)
- Pseudonymity is a goal of bitcoin.
- Consensus algorithm:
- New transaction broadcasts to all nodes.
- Each node collects transaction into a block.
- In each round a random node gets to broadcast its block.
- Other nodes accept the block only if all transactions in it are valid. (unspent, valid signatures)
- Nodes express their acceptance of the block by including its hash in the next block they create.
- Double spending attack is when an attacker tries to spend for example one(same) coin two times.
- Double-spend probability decreases exponentially with the number of confirmations from nodes. (most common 6 confirmations)
-
Malicious nodes can ignore the longest valid branch rule when proposing a new block.
- Proof-of-work
- Block reward - the node that creates a block makes a special transaction, which is a coin creation transaction, where it can select an address of the recipient, where it can add its own address to pay itself.
- Collection of the reward happens when the transaction will be confirmed by other nodes.
- Select node in proportion of computing power.
- Let nodes compete for right to create block.
-
Make it moderately hard to create new identities.
-
Attacks infeasible if majority of miners weighted by hash power follow the protocol.
- Formula that shows if it’s profitable to mine: if mining reward > hardware + electricity cost -> Profit
Can of worms
First I run a tutorial task to understand how it works. It was ransomware, which was encrypting the data on the computer and showed the message with information on how to pay the attacker in order to decrypt the data.

Then I picked the task Interactive analysis. ANY.RUN from a list of public tasks and it ran on a Windows machine. I chose FormBook trojan as an example of malware. FormBook is a data stealer that is distributed as MaaS (Mobility as a Service). MaaS integrates various forms of transport services into a single mobility service accessible on demand. (Source: What is MaaS?). FormBook is a well-known commercial malware, so dubbed because it has been sold “as-a-service” on hacking forums since 2016. (Source: Deep Analysis: New FormBook Variant Delivered in Phishing Campaign – Part I. FortiGuard Labs)

(I was trying to understand the tree of processes and how the trojan works, and I’m not sure if I got it correctly :) But this is what I understood)
On this screenshot we can see a list of processes, and look up how the malware acts step by step.
- User downloads and executes svchost.exe, which executes Coseismic.scr. An SCR file is a generic executable script created or used by a number of possible programs (Source: SCR File Extension - What is an .scr file and how do I open it?)
- After receipt.exe is executed it steals credentials from Web Browsers. Also it checks for supported languages on the system. Probably because it can show a message in the correct language to the victim, so the victim can pay to retrieve the data.
From this screen shot we can also see that the HTTP request was made by the receipt.exe process. And this HTTP request was checking for an IP address from http://checkip.dyndns.org/. Response body is <html><head>

On this screenshot we can see what kind of techniques and tactics this malware uses. For example we can see that the malware steals credentials from browsers and files (Credential access). Or in Execution we see that first of all the malicious file is executed by the user, but then the malicious file triggers Windows Command Shell to run the next steps (processes) of the mallwear.
Pick a StackExchange site related to the course, sort questions by score, and briefly explain one question and answer
I found a great explanation of the Heartbleed vulnerability on the ServerFault stackexchange openssl - How to explain Heartbleed without technical terms? - Information Security Stack Exchange.
Heartbeat was added to OpenSSL protocol to send “keep-alive” messages between client and a server to reduce requests amount that TLS requires to set up the connection. Heartbeat message contains a payload and the length of this payload. So when the client sends this Heartbeat message, the server saves the payload and a length in the memory. Then when the server sends a “keep-alive” response back to the client it reads those next 18 characters of memory starting from where it stored the payload and sends it back to the client (who checks that they received the right data back) and then the connection is kept alive. So the vulnerability occured, because server never checked for the length of the payload and does it really equal the length that was sent in this message. For example the client sends a short payload, but says that it’s maximum length (maximum value is 65535 bytes). So because the server never checks for the length of the payload itself, the server will start to send the response from where it saved the payload, and then 65635 bytes of additional information that is stored in the memory near the short payload message, such as passwords, emails and so on.
And the best way of explaining it:

H7
Bitcoin block structure
Each block contains a block header as well as transaction data — two crucial sets of information integral to the network’s proper function and ability to transfer value. Each block must also contain certain specific information in order to be recognized by the network and subsequently become properly validated and appended to the blockchain.
Screenshots are taken from Detailed Info about Block 614926. BitcoinChain.com

- Height - location of the block in the blockchain.
- Time - timestamp of the current block
- Hash - the hash of this block or a reference to the block
- Transactions - number of transactions in the block
- Output - how many bitcoins are in this block, sum of all the transactions.
- Fee - how much bitcoin was payed to the miner
- Main chain - Bitcoin’s main chain is the base blockchain layer where all transactions are processed and finalized. It basically means if the block was attached to the blockchain.
- Found by - the miner who solved the proof-of-work puzzle

- Difficulty - complexity to add the block into blockchain.
- Bits - The difficulty rating of the target hash, signifying the difficulty in solving the nonce.
- Size - size of the information in the block
- Version - field indicates the version number of the Bitcoin protocol being used.
- Nonce - contains a 32-bit number that a miner must alter in order to correctly solve the computational puzzle for the current block.
- Block reward - the amount rewarded to the miner for adding a block of transactions.
- Transaction fee - Every Bitcoin transaction spends zero or more bitcoins to zero or more recipients. The difference between the amount being spent and the amount being received is the transaction fee (which must be zero or more).
- Total output - how many bitcoins are in this block, sum of all the transactions. (same as Output from previous screenshot)
- Self hash - hash of the current block in the blockchain
- Previous block - hash of the previous block in the blockchain
- Next block - hash of the next block in the blockchain (empty on the screenshot, because it’s the last block)
- Merkle root - field contains a 256-bit hash of the root of the Merkle tree of all the transactions in the current block.
References
- Block (Bitcoin Block) Definition (investopedia.com)
- What Is a Block in the Blockchain? Block Structure. Gemini
- What Is Bitcoin Main Chain? - The Bitcoin Manual
- Miner fees - Bitcoin Wiki
- Structure of a Block in Blockchain - Naukri Learning
Usefull links
- https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists - collection of different lists for security assesments
- https://archive.org/ - archive
- https://www.wappalyzer.com/ tool for checking
- https://wiki.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_favicon_database - favicon database
- https://ui.ctsearch.entrust.com/ui/ctsearchui - certificates database
- https://crt.sh/ - certificates database
- https://crackstation.net/ - hashes library
Useful tools
- dnsrecon -t brt -d acmeitsupport.thm - bruteforce subdomain search
- ./sublist3r.py -d acmeitsupport.thm, https://github.com/aboul3la/Sublist3r - bruteforce subdomain search
Checks
- Try to input username, check if error returns “User with this username already exists” or “password is invelid for this username”
``` ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Usernames/Names/names.txt -X POST -d “username=FUZZ&email=x&password=x&cpassword=x” -H “Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded” -u http://10.10.87.232/customers/signup -mr “username already exists”
ffuf -w valid_usernames.txt:W1,/usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Passwords/Common-Credentials/10-million-password-list-top-100.txt:W2 -X POST -d “username=W1&password=W2” -H “Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded” -u http://10.10.87.232/customers/login -fc 200 ```
Terms
- IDOR - Insecure Direct Object Reference access control vulnerability
IDOR
If the Id cannot be detected using the above methods, an excellent method of IDOR detection is to create two accounts and swap the Id numbers between them. If you can view the other users’ content using their Id number while still being logged in with a different account (or not logged in at all), you’ve found a valid IDOR vulnerability.